Credit Cards are a part of our everyday life. We use plastic money to pay for our groceries, utility bills, shopping and many more. But have you ever wondered how a credit card actually works? What happens in those fractions of seconds when you swipe your card? How the money does reach merchant? And how many parties are involved in the payment process?
Using a credit card must be a simple process but the process of routing the payment is not. If we talk about- how a credit card function? Then, there are two different aspects to understand i.e. how a credit card functions financially and how does it work technically. Let us explore that tiny portion of time in detail through this article.
How a credit card works financially! (The broader view )
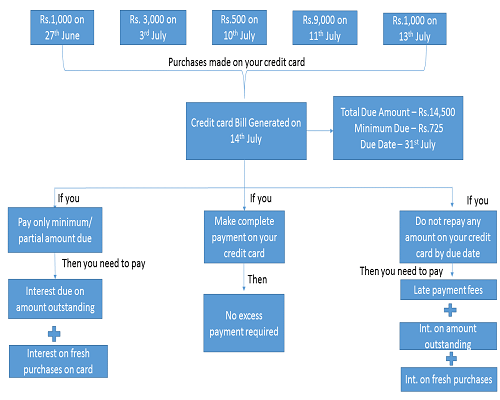
Each time you use your Credit Card, you are borrowing money from your card issuer (Bank / Credit Card Company). Every card issuer has a set due date, by which the borrower is expected to repay the complete amount due on their credit card. If the complete payment is made within that (interest-free) period, then no interest is charged by the credit card company. However, by that due date, if some portion of the due amount or complete amount does not reach the credit card issuer, then a pre-defined interest is charged on your previous dues as well as fresh purchases, till you do not repay the complete amount due on your card. Following is a pictorial representation of the way it works:
How a credit card works technically:
Before we understand the process to what happens when you swipe your Credit Card at the merchant location or enter card details for online shopping, let us first know the parties involved in the whole process.
a) Merchant: uses point of sale (POS) terminal to swipe the credit card
b) Acquirer: issues the POS machine to the merchant. An acquirer is a bank or financial institution that processes credit or debit card payments on behalf of a merchant. Ex: Axis Bank, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank etc. provide EDC machines to various merchants.
c) Credit Card Issuer: is a bank or credit card company who offers credit cards to people. Eg: HDFC Bank, Citibank, American Express, Standard Chartered etc.
d) Association: are also known as payment processing networks like Visa and MasterCard. American Express act as both the credit card issuers and the payment processing network.
e) Payment Gateway: is used when you shop online. It refers to an online application for authorizing credit card payments. It is the equivalent of a physical point of sale terminal located in most retail outlets.
When you swipe your credit card at merchant’s POS terminal, the merchant submits a request to the acquirer via a dial-up modem phone connection or a dedicated network connection. The acquirer then sends a request to the issuer to authorize the transaction. The credit card issuer verifies the cardholder’s account for available credit to cover the purchase. An authorization code is sent to the acquirer if sufficient credit is available. The acquirer authorizes the transaction and the cardholder receives the product.
Now, the way you shop, there must be hundreds of other customers also who swipe their card at same merchant location every day. To track their sales receipts each day, the merchant sends all these requests to the acquirer in batches. This batch is sent through the card network/ association (Visa/ MasterCard etc.) to request payment from the issuer (Bank/ card provider). The association thereby distributes each transaction to the appropriate issuer.
The issuer or the credit card company subtracts its interchange fees (ranges from 1% – 3% of transaction amount), which are shared with the association/ card network (Visa/ MasterCard), and transfers the amount to the acquirer. The acquirer, after keeping its margin (generally referred to as discount rate), transfers the remaining amount to the merchant.
So the merchant finally gets the amount after deducting around 1.5% – 3.5% of the sales value. The transaction rates may differ for each merchant based on the number of transactions, volume (in Rs.), type of transaction (monthly recurring, one-time payment, etc.) and category (retail, corporate, fuel, etc.). These rates are usually set by contract between the merchant and the acquirer.
The process is same for online shopping also except the payments are processed through payment gateways like VeriSign, PayUMoney etc. instead of POS terminals at merchant establishments.
At BankBazaar, we help you to pick the best credit card as per your need.
Dear Sir / Mam
I want to start Credit cards sales business in Lucknow.
Hi Bobby Yadav,
We’re sorry, but unfortunately we do not have much information regarding your query.
Cheers,
Team BankBazaar